About URL Encoder
URL encoder is an online tool that quickly encodes the given URL text. Also, it is more generally used within the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) set and it includes Uniform Resource Name (URN) and Uniform Resource Locator (URL). In addition, it is used in the preparation of data of the "application/x-www-form-urlencoded" media type.
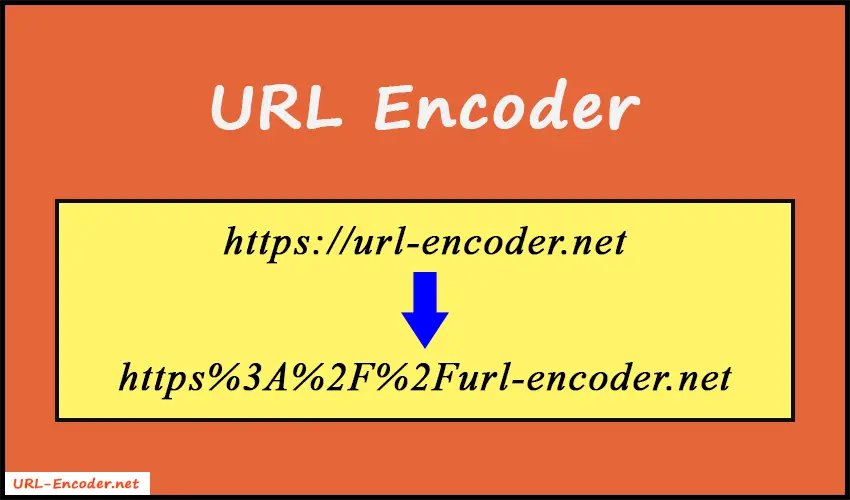
Even if you are a technical or non-technical person, the URL encoder is very simple to use. All you need to do is just type or paste the URL string in the input area and press the "Encode" button. As a result, the tool will automatically convert the text string into its URL encoded format and display on your screen.
What is URL?
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) is the address of a unique resource on the Web. A valid URL points to a unique resource. This resource can be an HTML page, CSS document, image, javascript, etc. Both the URL and the resources it is representing are handled by the online web servers.
A URL consists of different parts. Some are compulsory and others are optional. They are discussed below.
- Scheme: This is the first part that indicates the protocol that the browser must use in order to request the resource. The protocol is a method to exchange or transfer data around a computer network. In addition, websites generally use HTTPS or HTTP (the unsecured version of HTTPS) protocols.
- Authority: It is separated from the scheme by the pattern "://". Authority includes the domain and the port that is separated by ":". Domain represents the web server being requested. The port indicates the technical gate used to access the resources on the web server.
- Path to Resource: It is the path to the resource on the web server.
- Parameters: These are a list of key/value pairs separated by "&" used by web servers to do some extra stuff before returning the resource requested.
- Anchor: It represents a type of bookmark inside the resource, directing the browser to show the content stored at that spot.